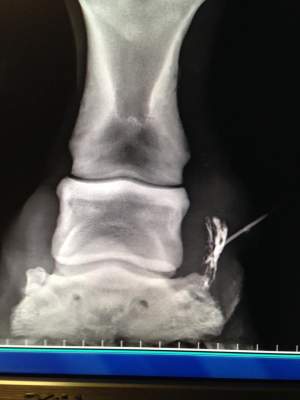
Quittor refers to damage to the collateral cartilage (sidebones) of the hoof. This condition generally occurs after an injury.
Quittor refers to damage to the collateral cartilage (sidebones) of the hoof. This condition generally occurs after an injury.
Cartilage has minimal blood supply making healing difficult. Infection usually follows, as in this case.
Quittor does not respond well to antibiotics. The lack of blood flow to the cartilage prevents delivery of the medication. Additionally, the body develops fibrous tissue to wall off the infection and prevent it from spreading. This inhibits the delivery of antibiotics.
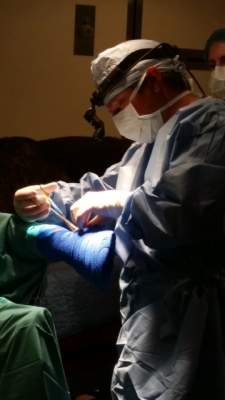
When antibiotics fail, surgical debridement is required to remove all dead and infected tissue, as in this case. A penrose drain is put in place to allow fluids to drain .